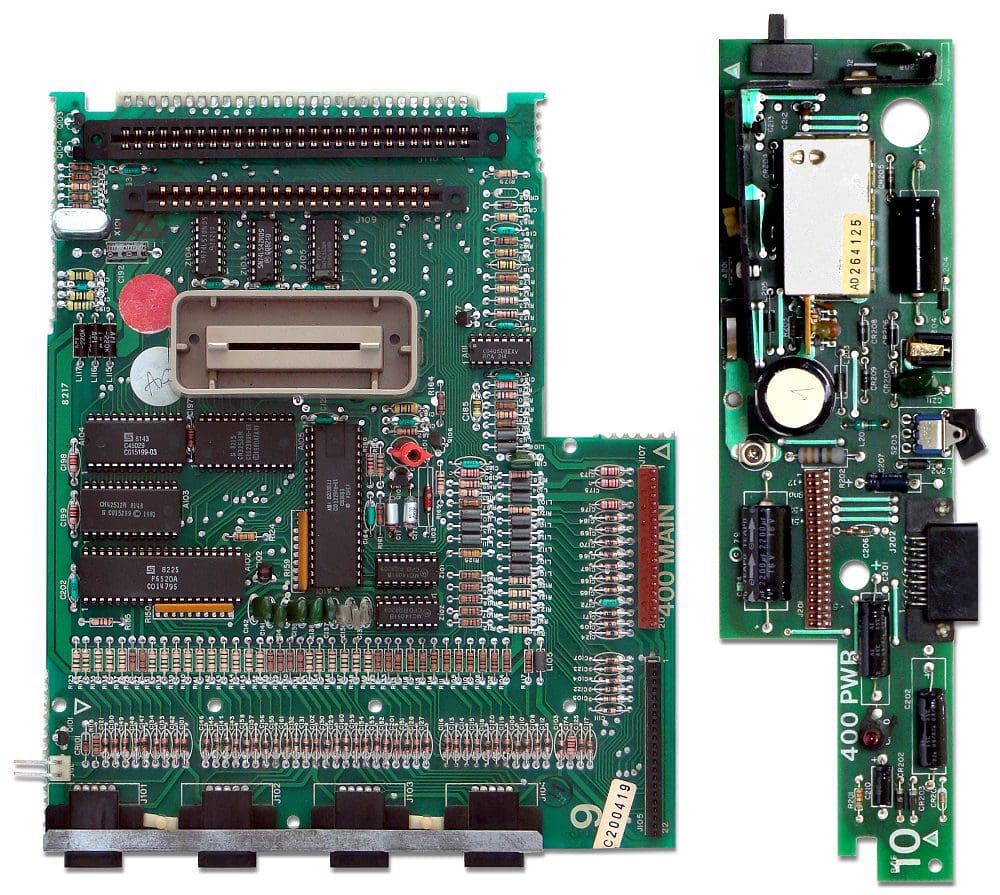
A motherboard is the spine of any computer, it connects every other component to the CPU. the motherboard also features a low of components itself. for example, the chipset is a critical communications platform for storage and peripherals. You’ve also got other necessary hardware such as the voltage regulator modules or VRMs and audio processing hardware. Despite the relatively large size of a motherboard, there isn’t really much free space. With all the components, connectors, and electrical traces connecting everything, motherboards are packed.
To be able to fit more components into a computer, features are added on separate circuit boards. These circuit boards that connect to the motherboard directly are called daughterboards. Daughterboards can even connect to other daughterboards. There’s a huge range of things that daughterboards can do and many different subcategories. Daughterboards can add big features, or can be a simple expansion of an existing feature. The key feature of a daughterboard is that it connects directly to another circuit board, via a socket, compared to using cables. So for example, an M.2 SSD that connects to a socket on the motherboard is a daughterboard. A 2.5-inch SATA SSD that connects via SATA cables would not be a daughterboard.

Uses for daughter boards
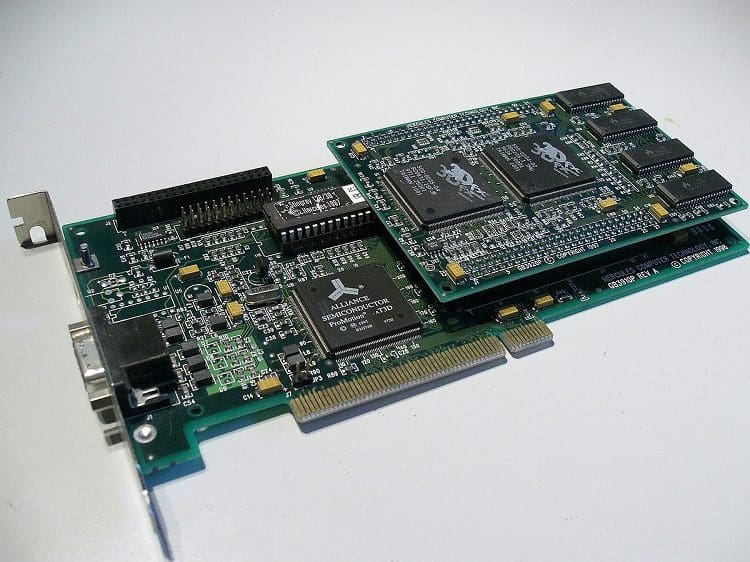
The most common example of a daughterboard would be RAM DIMMs. These connect via a socket near the CPU and provide access to high-speed Random Access Memory. Technically, even the CPU is a daughterboard as the CPU die is on a small circuit board that connects to the motherboard via a socket. As mentioned earlier, M.2 SSDs are an example of a daughterboard that adds storage capacity. Graphics cards are another common type of daughterboard connecting via a PCIe slot. These offer high-performance graphics and can complete other highly parallelisable tasks at great speed.
Some streamers may make use of a PCIe capture card to encode their stream video. There are many other examples of PCIe expansion cards or add-in cards, each of them is also daughterboards. The soundcard is an essentially obsolete daughterboard. They used to be basically required for high-quality audio, but modern motherboards offer perfectly acceptable audio and don’t cost extra or take up extra PCIe slots. Some sound cards even had optional daughterboards of their own. These were called wavetables, and they provided a range of instrument audio samples for use in MIDI mixing.
Network cards are another form of daughterboard. These often come in a standard PCIe add-in card format and provide ethernet ports. Some network cards may also offer Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity. Laptops and some desktops may make use of an mSATA socket to connect a tiny Wi-Fi or Bluetooth network card, though, again, some cards support both. These typically look like a really short M.2 SSD.
Form factors
In desktop computers, daughterboards are generally designed to stick out and away from the motherboard. This helps to leave plenty of space for other daughterboards and components. It also helps to ensure adequate airflow to the daughterboard to keep it cool. This airflow is especially critical for GPUs as they produce a lot of heat.
In laptops, the design concept is quite different. You can’t have large daughterboards sticking out from the motherboard and have a slim laptop. Laptops, therefore, typically use mezzanine cards, which lay parallel to the motherboard.
Both layouts have their advantages, typically cooling vs space efficiency. Not all daughterboards in desktop computers, however, will be placed perpendicular to the motherboard. The M.2 slot is almost exclusively parallel to the motherboard, as are the mSATA network cards. This is primarily because the standard is designed to be used in both laptops and desktops, and cooling isn’t a huge issue.

Conclusion
A daughterboard is a secondary circuit board that connects directly to the motherboard, or another circuit board via a socket rather than a cable. Daughterboards are present on virtually every computer in the form of RAM and CPUs. There are exceptions, such as mobile devices, where these components are typically soldered directly onto the motherboard. A daughterboard adds functionality to a computer without having to cram that functionality directly on the motherboard. The design concept means that you can have general-purpose motherboards that can be configured by the user with daughterboards rather than hyper-specific motherboard designs. The term daughterboard isn’t regularly used in modern times; however, it does still technically apply.