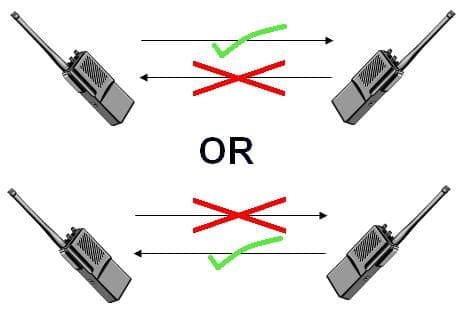
A lot of networking equipment will refer to its network connections as full-duplex or half-duplex. This term often isn’t explained, however, as it is assumed that people will know what it means. A duplex communication system is a system where two or more users can communicate in both directions.
Full-duplex
In a full-duplex system, both parties can communicate simultaneously. Both devices can send and receive data to and from each other at the same time.
A telephone is a well-known example of a full-duplex system, as both parties can speak and listen to the other user at the same time (regardless of their ability to understand one another while talking at the same time!)
Half-duplex
In a half-duplex system, both parties can still communicate with each other, however, only one user can transmit data at a time. For example, with walkie-talkies, a two way-radio system using push-to-talk buttons, a user can either listen or talk at any one time, not both.
A walkie-talkie defaults to being able to receive messages. If a user wants to communicate, they need to press the push-to-talk button, at which point their device is switched into transmit mode. When the push to talk button is released the device switches back into receiving mode. Other half-duplex devices operate in a similar manner, defaulting to receiving and only transmitting when they need to.
Tip: Devices that don’t require any form of duplex communication are referred to as simplex. In simplex systems, a device is either a transmitter or a receiver. Radio and TV are good examples of simplex technology.
Half-duplex systems are generally more simplistic in some ways. For example, only a single wire or radio-frequency is required for half-duplex communication channels. In comparison, a full-duplex system needs at least two wires or radio frequencies, one for transmission and one for receiving.
Collisions in half-duplex
The main issue with half-duplex systems is the risk of collisions, where more than one user or device attempts to transmit data at the same time. To prevent collisions, a collision-avoidance system, collision-detection system, or both need to be implemented.
In a collision-detection system, the transmitting devices will detect that a collision has occurred and pause transmissions for a random time before attempting to transmit again. This random pause is designed to avoid both devices attempting to re-transmit at the same time and colliding again.
In a collision-avoidance system, a device that wishes to transmit data checks if the network is free before transmitting. If the network is in use, it pauses for a random time before checking again.
Combining collision-avoidance and collision-detection systems is a generally effective way of managing half-duplex communications of networking gear and can cause negligible delays in most circumstances. In a manual system like with walkie-talkies however, the users have to perform this function manually, this has led to standards such as ending messages with the word “over”.