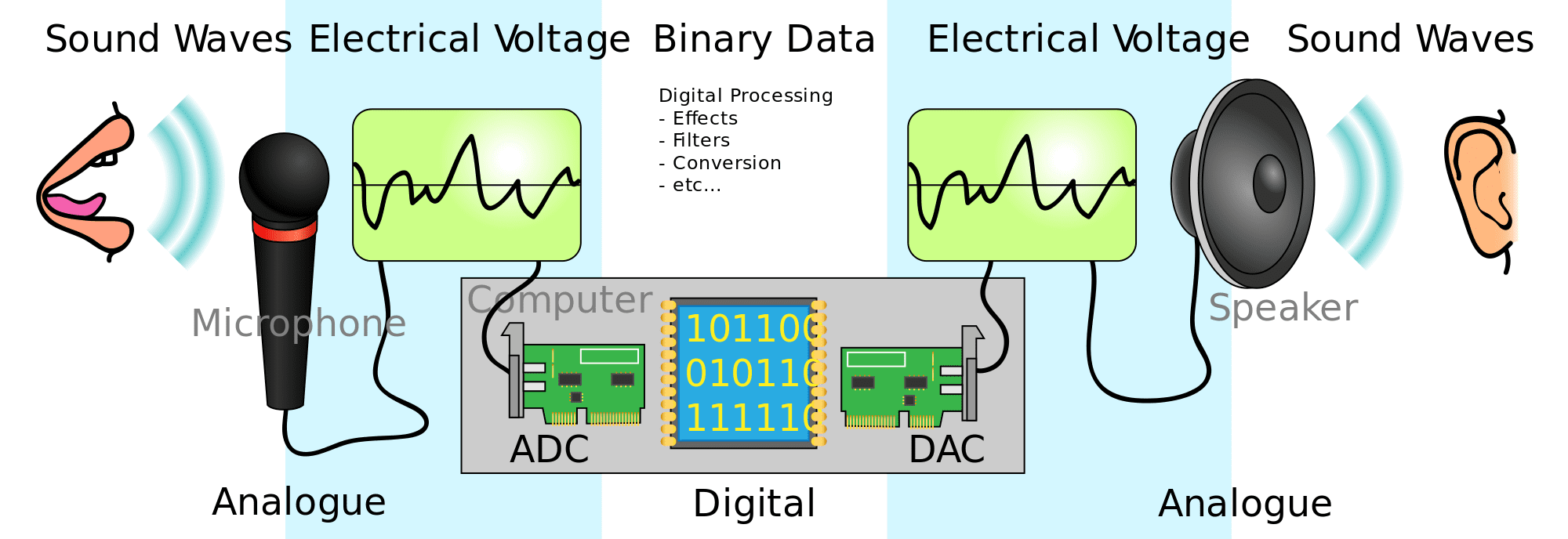
Codec is a portmanteau of coder-decoder, and is a device or computer program that encodes or decodes a digital data stream – typically an audio- image- or video file.
Hardware vs software
Hardware codecs are only really used for audio purposes. A hardware audio codec typically includes a DAC, Digital to Analogue Converter, and an ADC, Analogue to Digital Converter in a single device. This device can then convert sounds into a digital audio file and then play that audio file again as sound.
A software codec is a piece of computer software that can process the original source of data and convert it to a specific standard format so it can be easily read by other software that is configured to understand the relevant codec.
Lossy vs lossless
Codecs include compression in their processing, this is necessary as RAW file formats can be unreasonably large for long term storage or transmission over the internet. The inclusion of compression in codecs aims to reduce file sizes to a more manageable level.
Most codecs use lossy compression, which means that some quality of the resulting file is lost in the name of minimizing the file size. By using a high bit-rate, which includes more data per second, a lossy file can maintain a reasonably high level of quality while still not being unreasonably large. These types of codecs are ideal for audio or video files being streamed over the internet or stored on a home computer. The minimized file size means that your home internet can stream the data in real-time and that single files don’t fill entire hard drives.
Some codecs use lossless compression, which allows for the original file to be replicated with no data or quality loss. This is ideal for files that will still be processed, such as video and audio files that still need to be edited. If lossy codecs were used at each stage, the loss in quality would be compounded with each level of processing.