Say you’re attempting to use your computer to make a remote desktop connection with another computer, but are suddenly kicked out. You may be greeted with error code 0x3000008 and be wondering what on Earth just happened. This connection problem has a few causes, but we’ve got a few fixes to help you out.
In this article, we’ll be showing you how to fix error code 0x3000008.
Contents
What Causes This Error?
Error Code 0x3000008 is a connection issue that affects the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and is a result of failed authentication. Major causes of this failure are:
- An SSL or TLS handshake error, usually due to do with a lack of agreement on protocols or certification
- Failed credentials, such as an incorrect username or password
- Group Policy blocking communication
- Network, VPN, or firewall interference
How to Fix Error Code 0x3000008
When attempting a 0x3000008 error fix, there are a few different troubleshooting methods to try. Before doing anything else, though, first reboot the Remote Desktop Services and your PC if possible to see if the issue persists. It’s also a good idea to check your internet or network connectivity. Let’s get started:
Reset the Certificate
A major cause of error 0x3000008 is that of stuck, expired, or corrupted RDP certificates. Resetting this certificate is a quick, straightforward way to begin your troubleshooting journey. Here’s what to do:
Step 1. Open the Run Dialog (Win + R) and type “services.msc” into the box before hitting “Enter.”
Step 2. In the Services window, right-click on the following services and choose “Restart” from the context menu: “Remote Desktop Configuration,” “Remote Desktop Services,” and “Remote Desktop Session Host.”
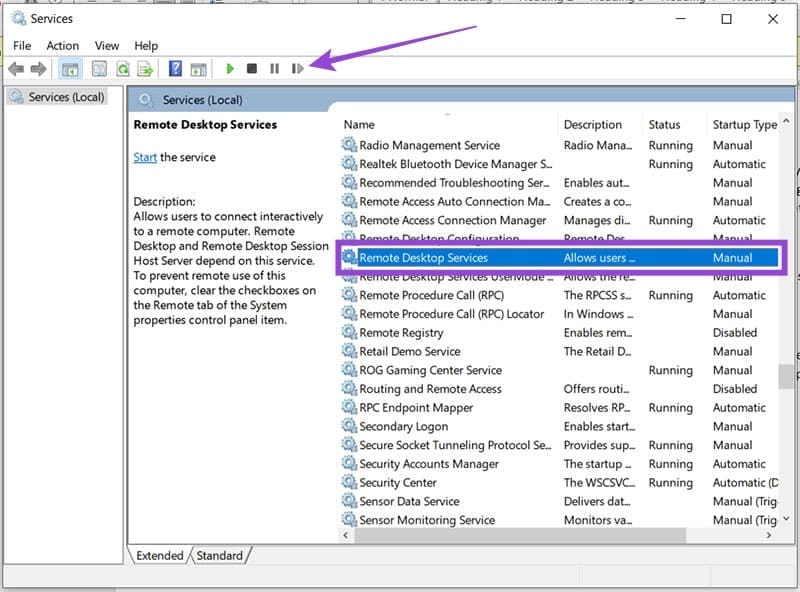
If the services aren’t running, you can click “Start” in the context menu before selecting “Restart.”
Next, you will need to delete the current SSL certificate, so your machine can create a new one. To do this, you’ll need to enter the Registry:
Step 1. Open the Run Dialog and type “regedit” before hitting (Ctrl + Shift + Enter) to run as Admin.
Step 2. Enter the following path enter the address bar at the top of the window: “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp”.
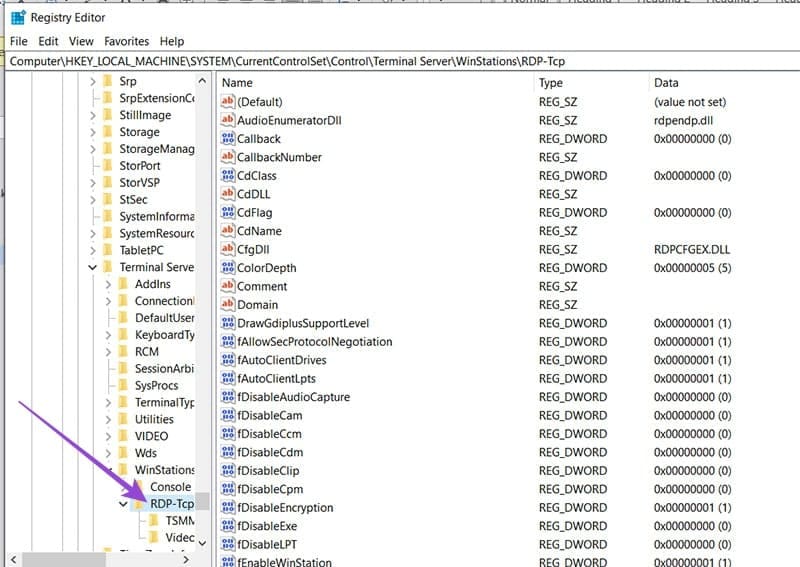
Step 3. Navigate down to “SSLCertificateSHA1Hash,” click it, and press the (Del) key to remove it.
Step 4. Reboot your device, and Windows will recreate a new certificate.
Disabling SSL/TLS 1.0
Older protocols might still be in use on your machine, and these are often blocked by newer Windows security updates or antivirus software. To fix this, you can disable them in the Registry:
Step 1. Open the Run Dialog, type “regedit” and press (Ctrl + Shift + Enter) to run as Admin.
Step 2. Navigate to the following location: “Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp.”
Step 3. Right-click the “RDP-Tcp” folder in the sidebar and select “New” and “DWORD (32-bit).”
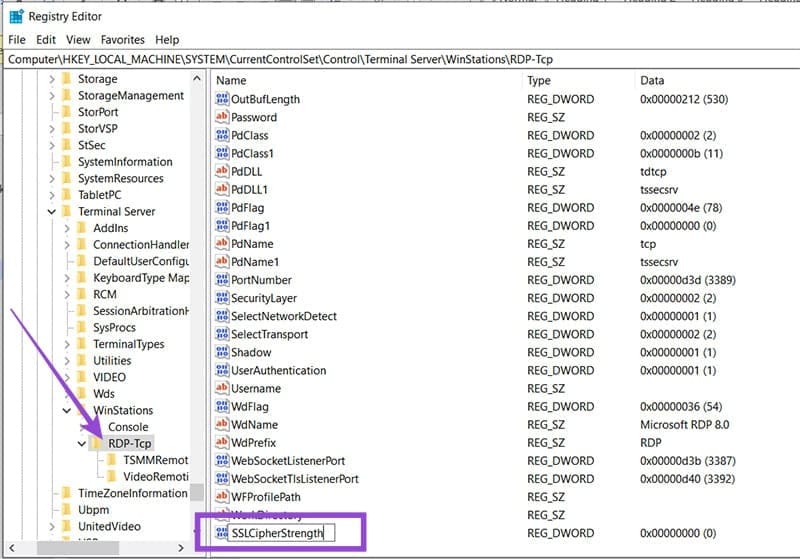
Step 4. Name the new DWORD “SSLCipherStrength.”
Step 5. Double-click the new value and set the “Value data” to “0” and the “Base” to “Hexadecimal.”
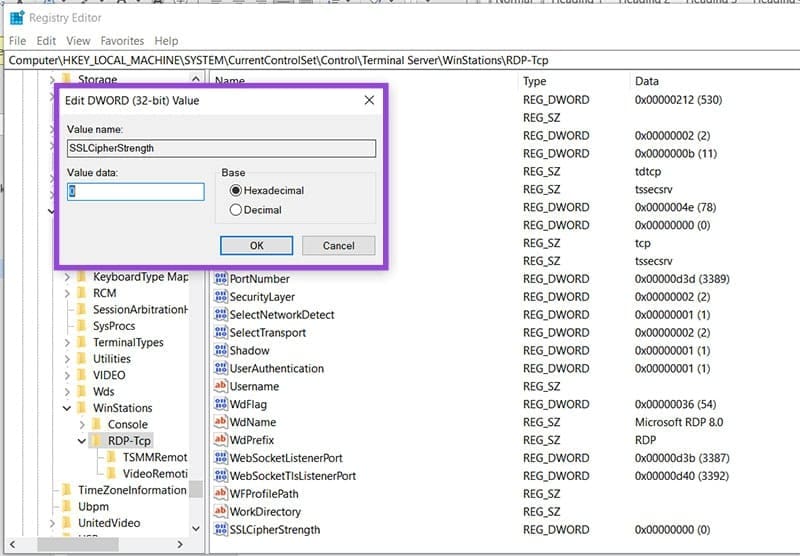
Step 6. Click “OK” to finalize, then reboot the machine.
Delete the Terminal Server Client Cache
Corrupted cache data is always a major cause for malfunctions and errors in software, and Remote Desktop Services is no exception. Thankfully, clearing the cache is an easy job:
Step 1. Open an Explorer Window (Win + E) and click on your main drive (usually “C:”).
Step 2. Navigate to “Users,” your profile name, and select “App Data.”
Step 3. Click “Local” and then “Microsoft.”
Step 4. Navigate down to “Terminal Server Client,” then click on “Cache.”
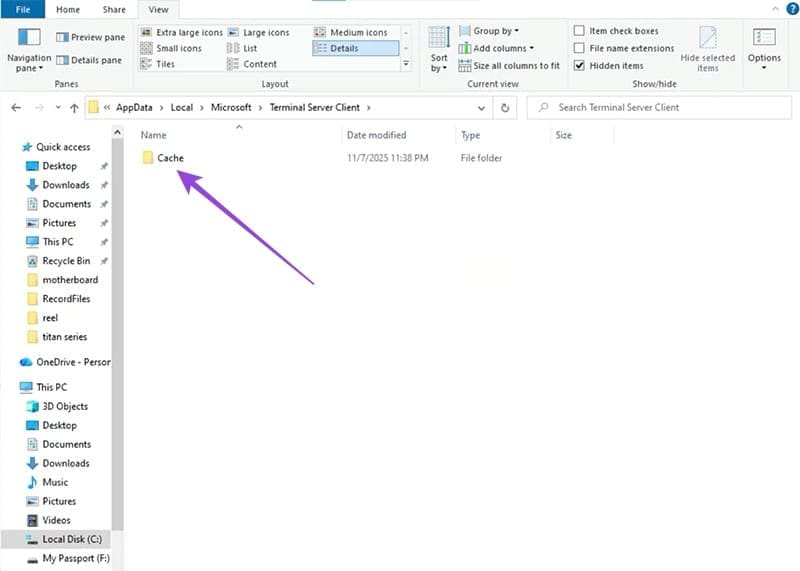
Step 5. Delete all files in this folder by selecting them all and pressing (Ctrl + Shift + Del) to skip sending them to the Recycle Bin.
Step 6. Restart your machine. Windows will automatically recreate the files.