If you’ve tried to create, edit, or rename a file or folder then suddenly hit with the “Error 0x800700CE: The filename or extension is too long,” you may be wondering what on earth to do. This error isn’t always the result of a lengthy filename, but can also be caused by a few other issues too.
In this article, we’ll be supplying a few possible fixes, so you can get things back to normal.
Contents
What Causes Error 0x800700CE?
Let’s start with the obvious off the bat. The most likely cause of this error is the filename length. Windows has historically capped its filenames at a length of 260 characters. The cloud service OneDrive, allows up to 400 characters. The NTFS file system on Windows does allow for longer character names (over 32,000), but many programs and APIs enforce the original limit to avoid issues.
In addition, here are a few other causes of the error:
- File and registry corruption
- Syncing issues between online and PC storage
- An overzealous antivirus
- Problems with a new or outdated version of Windows
Fix Error 0x800700CE With These Solutions
We’ve looked at the “whys,” so now for the “hows.” Try these solutions below and see if your problems are solved:
Rename Your File or Folder
Let’s start simple. If only one or two files or folders are triggering this error, then it may be worth changing the file name just to see. Make sure that it fits under 260 characters (which includes spaces and symbols) and check to see if the issue is resolved.
Run the File and Folder Troubleshooter
The free Windows File and Folder Troubleshooter is a convenient utility and way to check for issues that might not be related to the length of your file or folder. You can run it like this:
Step 1. Download the troubleshooter and run it.
Step 2. Click “Next” and check the “Renaming or moving files or folders” option and any others that may apply.
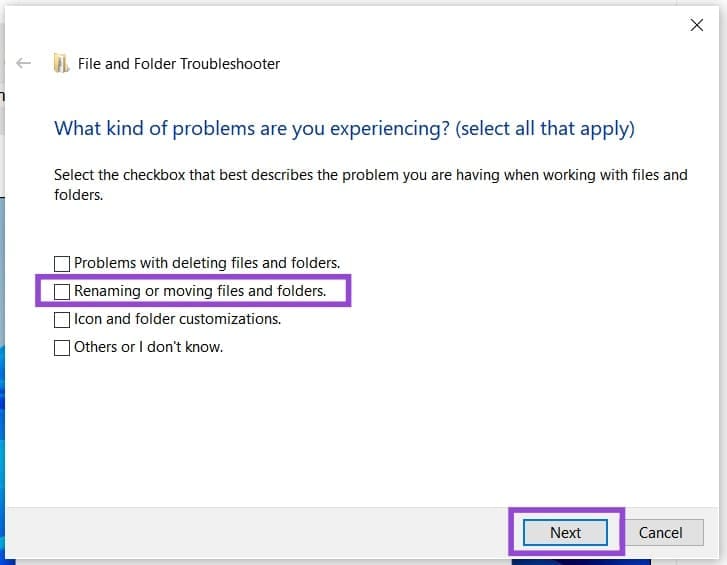
Step 3. Click “Next” and let the troubleshooter run.
Step 4. Restart your machine and see if the issue is resolved.
Enable Longer File Names
One way around the issue is to make the Windows naming rules fit your own. As mentioned above, the NTFS file system does allow for longer file pathing names. You’ll just have to enable it through editing the Group Policy Editor. Ensure you have admin privileges and do the following:
Step 1. Type “group policy editor” into the search bar and click the option that pops up.
Step 2. In the Local Group Policy window, click “Administrative Templates” under “Computer Configuration.”

Step 3. Navigate to “System” and then “Filesystem.”
Step 4. In the main window, double-click “Enable Win32 long paths.”
Step 5. In the window that pops up, check the “Enabled” option, and click “Apply” and “OK.”
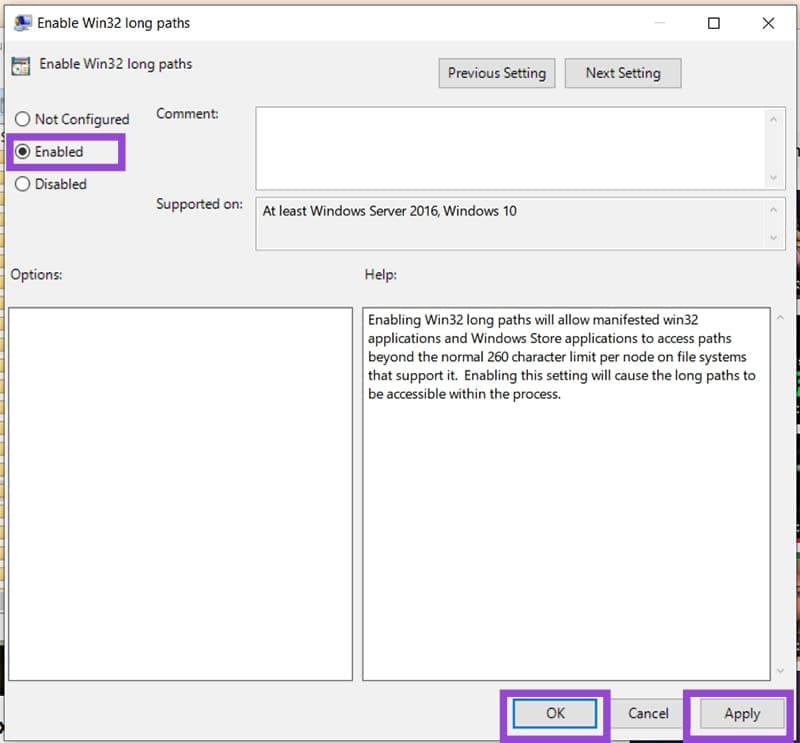
Step 6. Restart your machine and see if the issue is resolved.
Rename Files with Command Prompt
If you’re looking for a way to bypass limitations on individual files, then you can rename them via Command Prompt. Here’s what to do:
Step 1. Open the Run Dialog (Win + R) and type in “cmd” into the dialog box provided. Press (Ctrl + Shift + Enter) to run as Administrator.
Step 2. In Command Prompt, enter the name of your old file and the new one in this format: ‘ren “Old” “New”’ and press “Enter” once done.

Step 3. See if the change takes place.