Lidar is a technology that is often included in projects such as self-driving cars. The name Lidar has multiple meanings, although the concept they describe is all the same. The name originally came from a portmanteau of “light” and “radar”, but it has since been given the backronyms “light detection and ranging” and “laser imaging, detection, and ranging”.
How does lidar work?
Lidar uses one or more laser beams to generate a high-resolution distance measurement. The lasers being used can vary between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared, with specific wavelengths chosen depending on the task being performed.
When the laser beam hits a surface, some of the light is reflected back to the device through backscattering. This reflected light is then detected with a time-of-flight camera which determines distances by the time it takes the reflected light to reach the detector.
Tip: Backscattering is the type of reflection that happens from most surfaces. Specific reflectors such as mirrors may redirect most incoming light in one specific direction, but most materials scatter the reflected light in all directions.
One limitation of lidar is that it is limited to a direct line of sight, it is only able to detect the presence of the first object that the laser encounters in any specific direction. This means that all objects cast a blind-spot shadow behind them and thus can easily miss even just slightly hidden objects.
Uses of lidar
In a typical scanning lidar configuration often found on self-driving cars, the laser source is mounted on top of the car in a casing that spins rapidly. This design allows the car to generate a full 360-degree distance measurement, so it knows if there are any objects that are too close. The rapid rotation also allows for these distance measurements to be performed many times a second, allowing for real-time adjustments to a situation that can rapidly develop. Typically, multiple lasers are used, or the laser beam is split to allow the device to scan a range of heights in one pass.
Lidar devices are also mounted on aircraft or satellites to perform surface mapping operations. With specific laser frequencies, lidar is also capable of mapping the depth of the seafloor, although the resolution is somewhat reduced. These perspectives can also be used to monitor cloud coverage and the presence of some pollutants such as aerosols. satellite usage isn’t limited to earth-bound probes. Lidar can also be mounted on deep space missions and used for both range-finding and mapping the surface of other planets, moons, and other bodies.
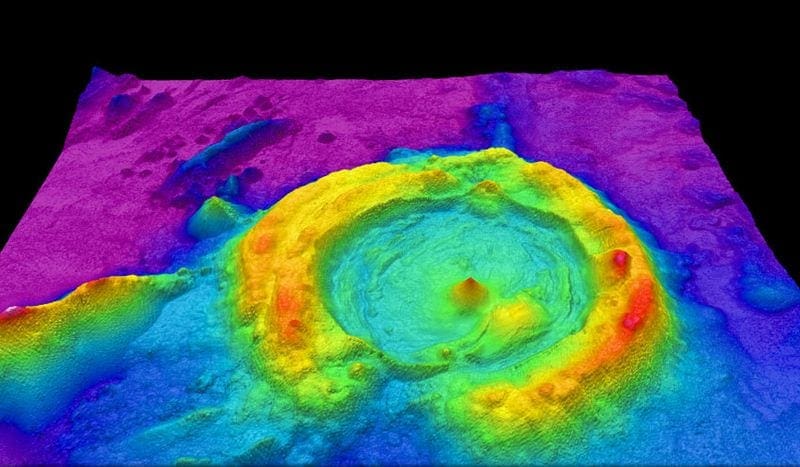
Lidar can be also be used from multiple stationary perspectives to generate an extremely accurate three-dimensional model of an area. This is especially useful for architectural and construction uses but also has other uses such as crime scene reconstruction.